Curation Jobs
Curation Jobs automate the ongoing process of maintaining specific clinical datasets by continuously identifying patients who meet your selection criteria, extracting relevant clinical data, and keeping your dataset up to date. Unlike one-time extractions, curation jobs run on a schedule you define, ensuring your datasets stay current as new clinical data arrives.
What Are Curation Jobs?
Building a clinical dataset isn't a one-time task—it's an ongoing process. Patients receive new diagnoses, undergo procedures, start medications, and accumulate documentation over time. Curation Jobs address this reality by automating the continuous discovery and extraction workflow.
Instead of manually re-running extractions or wondering whether your dataset reflects the latest patient data, you configure a curation job once and let it run automatically. The job identifies patients matching your inclusion and exclusion criteria, extracts the clinical data elements you've specified, transforms the data according to your schema, and generates reports showing what was found and processed.
This automation ensures your datasets remain current without manual intervention, making them reliable sources for ongoing quality reporting, research studies, and clinical decision support.
Setting Up a Curation Job
Creating a curation job follows a four-step guided process that takes you from selecting your extraction schema to launching the automation.
Step 1: Ontology Configuration
Start by choosing the ontology that defines what clinical information to extract and how to structure it. The ontology serves as your extraction schema, specifying which fields to capture, what data types to expect, and what extraction logic to apply.
Browse the available ontologies and select the one that matches your dataset needs. The system displays each ontology's configuration, including its fields, categories, and extraction guidelines. Whether you're building a cancer registry requiring detailed staging information, a chronic disease cohort needing medication and lab data, or a custom research dataset, you'll find or create an ontology that structures your data appropriately.
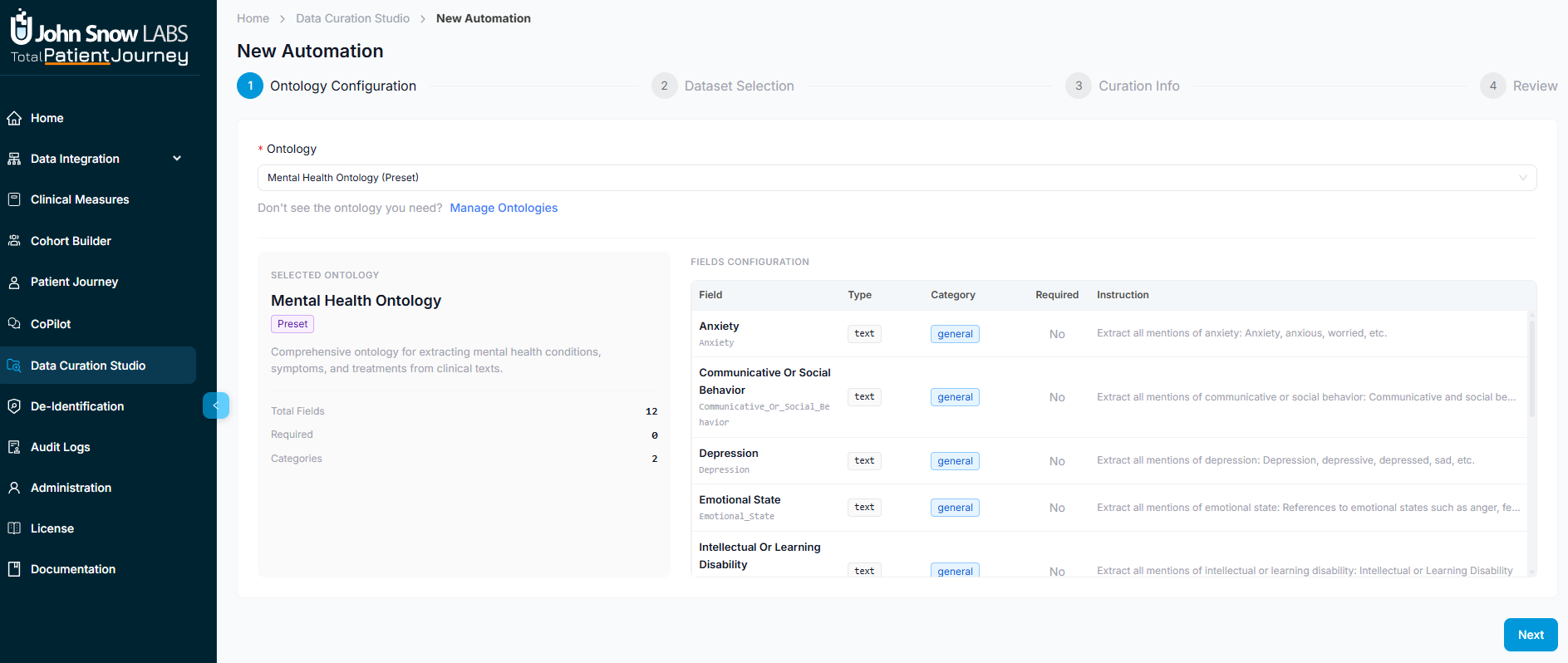
Step 2: Dataset Selection
Next, select the dataset containing the patients and documents you want to process. This determines which population will be evaluated against your ontology's extraction criteria.
You can choose from existing cohorts, patient lists, or document collections already defined in the system. For example, you might select a cohort of patients with specific diagnoses, a group identified through previous queries, or a document set filtered by type and date range.
The dataset selection defines the scope of your curation job—only patients and documents within this dataset will be processed during extraction. This ensures you're targeting the right population without processing unnecessary records.
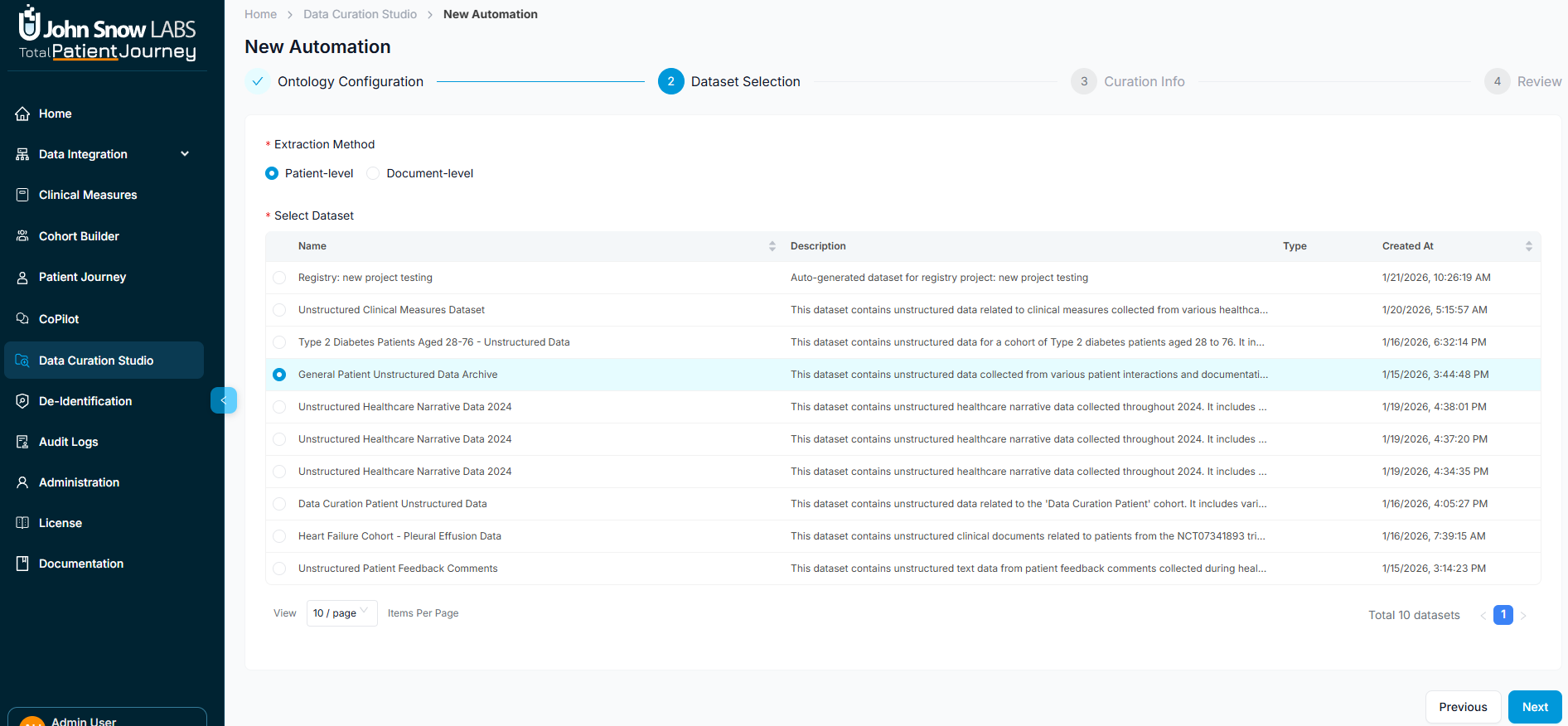
Step 3: Curation Information
Provide essential metadata about your curation job. Give your automation a descriptive name that clearly identifies its purpose: this name will appear in your dashboard and reports, so choose something meaningful like "Q4 2024 Breast Cancer Registry" or "Diabetes Cohort - Weekly Update." This will also specify the target database where extracted results will be stored. This determines where curated data becomes available for downstream analytics, reporting, and research use.
Optionally, add a detailed description explaining the curation job's purpose, scope, or any special considerations. This documentation helps team members understand the automation's intent and supports knowledge transfer as your curation automation grows.
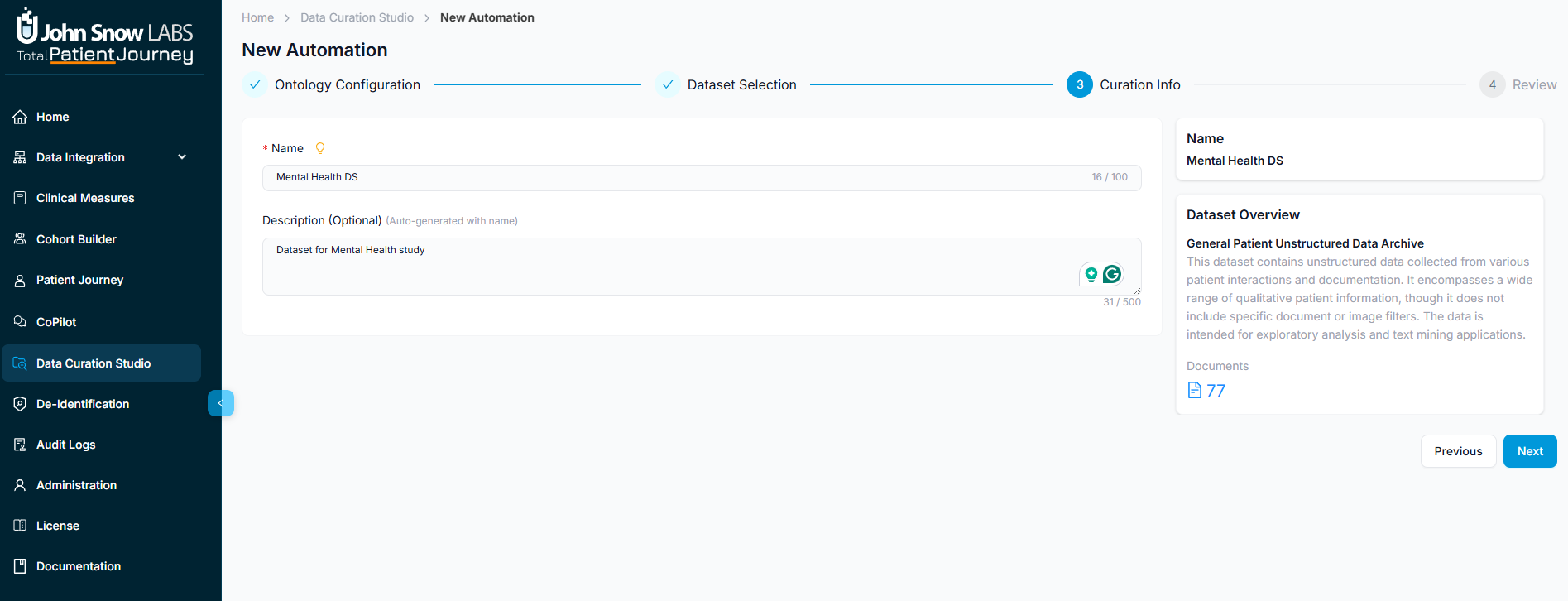
Step 4: Review and Launch
Before execution begins, review your complete automation configuration. The system presents a summary showing your selected ontology and its field count, the chosen dataset with patient and document counts, the target database for results, and any metadata you've configured.
This review step ensures everything is configured correctly before you commit computational resources to the extraction. Verify that you've selected the right ontology, targeted the correct population, and specified the appropriate storage location.
When everything looks correct, click the start curation button to launch the automation. The job begins processing immediately, applying your ontology's extraction logic to the selected dataset and storing structured results in your target database.
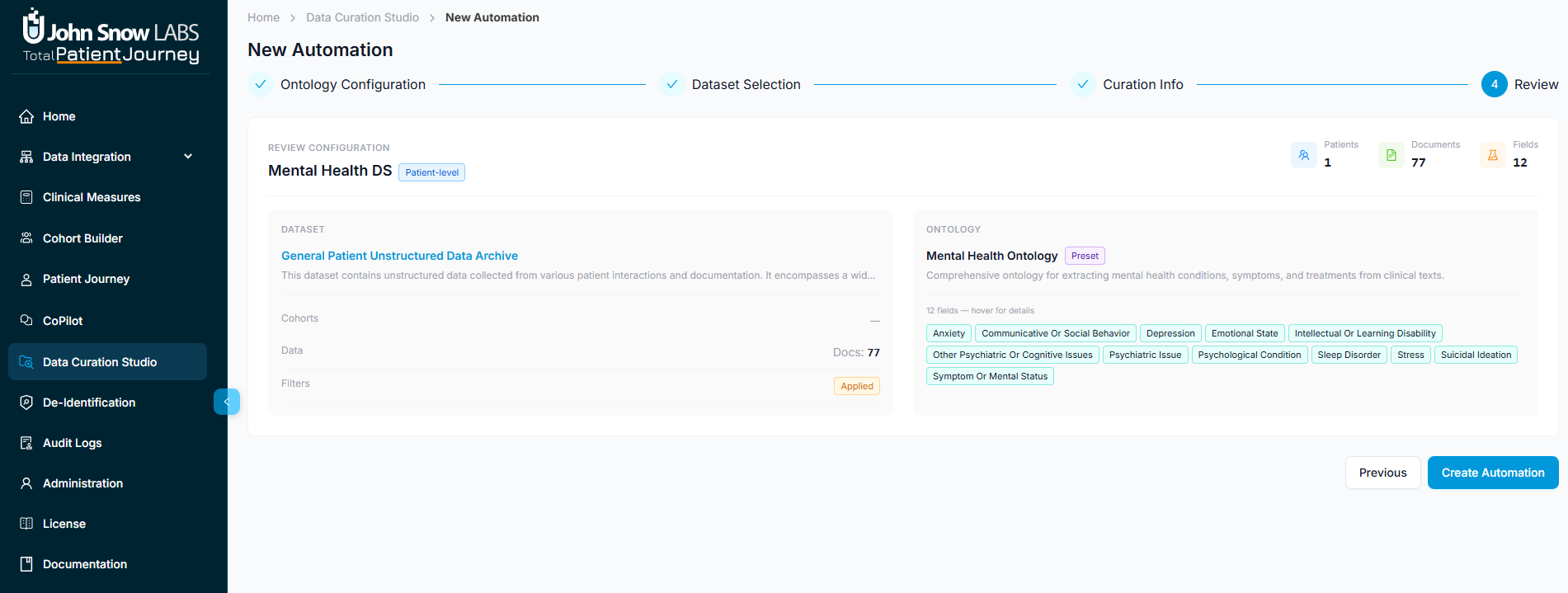
Monitor Job Results
After each execution, review the job logs and statistics to understand what the automation accomplished. You'll see how many patients were identified, how many records were extracted, any errors or warnings encountered during processing, and summary metrics about the extracted data.
This monitoring capability helps you verify that jobs are running as expected, identify any issues requiring attention, and track registry growth over time. Regular review of job results ensures your automated curation remains accurate and complete.