Platform Architecture
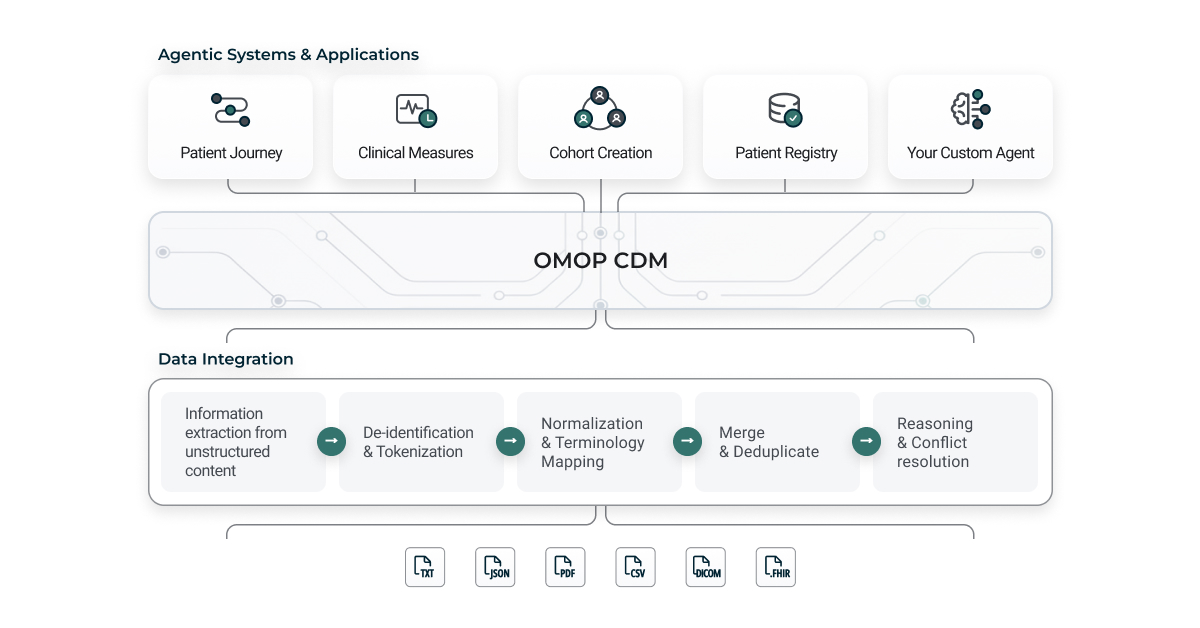
Architectural overview of the Patient Journey Intelligence platform showing data flow from source systems through processing layers to analytics applications.
Healthcare data is messy. It arrives as free text buried in clinical notes, as scanned PDFs from decades-old paper records, as structured extracts from multiple EHR systems that don't speak the same language. And yet, if we want to build AI systems that can genuinely help patients and clinicians, we need to transform this chaos into something coherent, standardized, and trustworthy.
That's the challenge Patient Journey Intelligence was designed to solve. At its core, the platform takes real-world clinical data across every modality you can imagine and converts it into AI-ready patient journeys that maintain full transparency about where each piece of information came from, how confident we are in it, and how it evolved over time.
Three Layers, One Journey
The platform is organized into three foundational layers, each building on the work of the one below it. Together, they transform fragmented clinical data into complete patient stories that AI systems can actually work with.
Layer 1: Data Curation—Making Sense of the Mess
The first layer is where the hard work of data curation happens. Think of it as the foundation that everything else depends on. Real-world clinical data arrives in every format imaginable: free text notes written by busy clinicians, scanned PDFs from decades-old paper charts, structured extracts from EHR systems, DICOM headers from imaging studies, FHIR resources from modern APIs, and claims data with ICD-10 and CPT codes. This layer ingests all of it and applies a governed curation workflow to transform chaos into clarity.
Multimodal Information Extraction is the first step. The platform pulls clinical meaning from unstructured text like clinical notes and discharge summaries, runs OCR on scanned documents to extract text from historical paper records, parses imaging metadata from DICOM headers, validates structured fields like labs and vitals from EHR extracts, processes claims and billing codes, and ingests standards-compliant FHIR resources. Every modality gets processed, and every piece of clinical information gets captured.
Next comes de-identification and tokenization, where privacy protection is applied consistently across everything. The platform removes protected health information in compliance with HIPAA standards, applies consistent pseudonymization using secure hashing so records can be linked across datasets, shifts dates while preserving temporal relationships and seasonality, and supports configurable de-identification profiles for different use cases like research, quality improvement, and registries.
Then terminology normalization and mapping takes over. Entities extracted from unstructured documents and entities imported from structured content all get standardized to medical vocabularies. The system currently supports SNOMED CT for conditions, procedures, and clinical findings, RxNorm for medications and drug ingredients, LOINC for laboratory tests and clinical measurements, and ICD-10-CM for diagnosis codes.
Patient-level merge and deduplication consolidates clinical events across sources and time. Record linkage identifies duplicate or overlapping events from different systems, and representations of the same clinical fact get merged into one record.
Finally, clinical reasoning and reconciliation applies intelligent logic to resolve ambiguity and conflicts. The platform estimates confidence using ML-based scoring of extraction certainty for each clinical fact. It reconciles conflicts automatically when different sources provide contradictory information. It distinguishes assertion status—is this a confirmed diagnosis, a ruled-out condition, family history, or a patient-reported symptom? And it applies temporal reasoning to understand how assertions change over time, like the difference between "history of diabetes" and "current diabetes."
Rather than producing opaque outputs, this layer explicitly captures how each clinical fact was derived, which sources contributed, how conflicts were resolved, and how confidence evolves over time as new data arrives. The output is curated, standardized clinical facts with full provenance, confidence scores, and temporal context, ready for transformation into standardized data models.
Layer 2: AI-Ready Data Assets—Building Living Datasets
The second layer is where curated clinical facts become AI-ready data assets. The platform's core function is to manage and continuously update one or more of these assets, each built by combining all available data about each patient across modalities and sources into coherent, longitudinal representations.
OMOP CDM v5.4 standardization is a key example. The platform transforms curated clinical facts into OMOP Common Data Model v5.4, which enables interoperability with the broader research ecosystem and supports transparent validation and quality assurance. Standard vocabularies like SNOMED CT, RxNorm, and LOINC are prioritized, with reconciliation of local or non-standard codes through concept relationships.
But the platform's scope goes beyond producing a static schema. Each AI-ready data asset is maintained as a living dataset with four critical characteristics. First, there's end-to-end provenance—full lineage from raw source document to final patient-level assertion. Second, confidence scores and reasoning metadata capture ML certainty and clinical reasoning for each fact. Third, versioning and audit readiness track model versions, logic versions, and data refreshes over time. And fourth, the platform transparently handles data evolution, explicitly addressing conflicting, missing, or decaying data points as they change.
Multiple datasets can run in parallel, all kept consistent and in sync. Common examples include an identified OMOP patient journeys dataset for operational use, supporting care coordination, quality improvement, and point-of-care AI. There's a de-identified OMOP patient journeys dataset for research, model development, and external collaboration that's HIPAA Safe Harbor compliant. And there are disease registry and real-world evidence dataset modules optimized for specific use cases like NAACCR cancer registries, abstraction workflows, and evidence generation.
Because these datasets share large portions of the underlying curation workflow, maintaining them in parallel is significantly more efficient than building each independently. This design also enables seamless progression from research to production—a model developed on de-identified data can be deployed against identified patient data without rewriting logic, because both the syntactic and semantic data models remain aligned.
The output of this layer is multiple synchronized, living AI-ready datasets with full provenance, confidence, and versioning.
Layer 3: Agentic Systems and Applications—Putting Data to Work
The third layer is where AI-ready data assets become useful. On top of the standardized patient journeys, the platform supports a growing ecosystem of agentic systems and applications.
The platform includes pre-built agents like a cohort builder that demonstrate how standardized patient journeys can be operationalized quickly. But it's also designed to empower data science and data engineering teams within academic medical centers, healthcare IT companies, and life science organizations to build their own AI agents and applications on a shared, production-ready foundation. This lets teams focus on innovation rather than data plumbing, while inheriting scalability, compliance, and governance by default.
Example agents and use cases show what's possible. Clinical trial matching agents operate on fully identified datasets with access to complete, up-to-date multimodal patient journeys for real-time eligibility screening. Risk adjustment and care gap agents identify patients with documented diagnoses present in clinical narratives but missing from problem lists, supporting improved HCC scoring, HEDIS measures, and audit-ready recommendations with full provenance for each finding. Patient Co-Pilot assistants provide conversational interfaces that answer clinical questions about individual patients using complete longitudinal data. And registry automation agents automatically abstract cases, calculate staging, and generate regulatory reports for cancer registries and quality programs.
All agents consume the same governed data assets, ensuring consistent results and transparent justification across applications. The outputs include clinical insights, cohort definitions, quality measures, AI-powered recommendations, and custom analytics.
Governance and Quality—Trust Through Transparency
Healthcare AI systems need to be trustworthy, and trust comes from transparency. That's why governance and quality aren't afterthoughts in Patient Journey Intelligence—they're built into every layer of the platform architecture.
Data quality monitoring runs continuously across all ingestion and transformation stages. Completeness metrics track record counts and field coverage to ensure comprehensive data capture. Automated validation rules enforce data integrity at every processing step. Built-in anomaly detection identifies unexpected patterns or outliers that may indicate data quality issues. And interactive quality dashboards provide real-time visibility into the health and completeness of your clinical datasets.
Auditability ensures every clinical fact maintains complete provenance from its source document through extraction to its final OMOP representation. Source-to-OMOP lineage tracking lets you trace any data point back to its origin. Extraction confidence scoring provides transparency into the certainty of AI-derived facts. All user actions are logged for compliance and troubleshooting purposes. And version control maintains historical records of ontologies, mapping rules, and extraction models, ensuring reproducibility and supporting regulatory audits.
Privacy and security are integrated into every layer of the platform. De-identification workflows automatically remove protected health information in compliance with HIPAA standards. Role-based access controls ensure users only access data appropriate to their role and authorization level. Comprehensive audit trails track all PHI access for compliance reporting. And enterprise-grade encryption secures data both in transit and at rest, meeting stringent healthcare security requirements.